- Doosan Enerbility
- Doosan Bobcat
- Doosan Mottrol
- Doosan Fuel Cell
- Doosan Tesna
- Doosan Robotics
- Doosan Mobility Innovation
- Doosan Logistics Solutions
- Doosan H2 Innovation
- Doosan Investments
- Oricom
- Hancomm
- Doosan Magazine
- Doosan Bears
- Doosan Cuvex
- Doosan Corporation Electro-Materials
- Doosan Digital Innovation
- Doosan Corporation Retail
- Doosan Yonkang Foundation
- Doosan Art Center
- Doosan Business Research Institute

Press Release
- Also signed “Engine Layout Design and Analysis Service Agreement” this past June as part of efforts to diversify gas turbine business
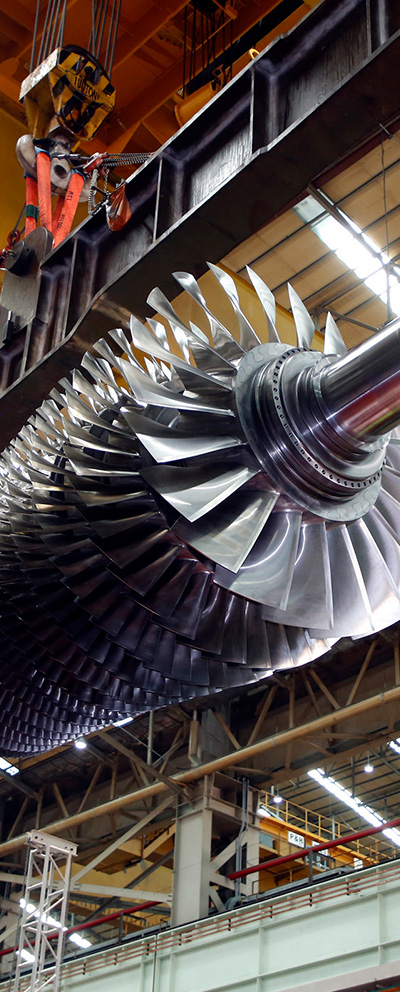
Doosan Enerbility, which is recognized as being the fifth in the world to have successfully developed a gas turbine for power generation, is now seeking to further diversify its business by participating in the manufacturing of key components for aircraft gas turbine engines.
On August 21st, Doosan Enerbility announced that it had signed an agreement with the Agency for Defense Development on the “Manufacturing & Post-Treatment of Turbine Vane & Blade Casting Parts.” Doosan will be manufacturing the turbine blades and vanes,* essential hot parts of the aircraft gas turbines currently being developed by the Agency for Defense Development, and will be supplying it to the agency by 2027.
*Blades are the rotating airfoils that are connected to a gas turbine’s central axis (rotor) and vanes are stationary airfoils positioned between the turbine blades which perform the function of bringing together the air flow which had dispersed after passing through the turbine blades.
This contract is part of the “Component Technology Development for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Turbofan* Engine” project, a project that is currently being carried out by the Agency for Defense Development. Doosan Enerbility had previously signed another contract this past June with the agency agreeing to provide aircraft turbofan engine layout design and component analysis services.
* Aircraft gas turbine engines can be classified into the turbojet, turbofan, turboshaft and turboprop engines. Most aircrafts adopt the turbofan engine assembly method. Within a turbofan engine, there is a single fan that is used to suck in the air and two paths of airflow. One airflow passes through the engine core (combustion chamber), while the other one bypasses the engine core and flows on the outside of the engine (bypass air).
The gas turbines for aircrafts and power plants are based on the same technology and thus, the operating principles and structure are found to be similar. Given that the main objective of aircraft gas turbines is to generate thrust to propel the aircraft through the air, high power output, lightness in weight and operational flexibility are essential criteria in the design. As for power plant gas turbines, since the main objective is to achieve high efficiency, high power output and stability, the larger size of these gas turbines is the main differentiating feature.
”This recently won project is quite significant in that we were able to use our technical expertise in designing and manufacturing gas turbines, something that was achieved via local industry- academia-research sector cooperation, to expand our reach to the aircraft engine sector as well,” said Hongook Park, CEO of Doosan Enerbility’s Power Services Business Group. He added, “We will be leveraging the technology and systems that we obtained over the years from developing power plant gas turbines and will be applying this now in the development of gas turbines for aircrafts.”